
In today’s digital age, websites serve as the digital storefronts for organisation. With the increasing prevalence of cyber threats and attacks, ensuring the security of your website has become more critical than ever.
One of the fundamental aspects of website security is the implementation of SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the importance of website security. We’ll explain the difference between HTTP and HTTPS, and the dangers of not securing your site with an SSL certificate.
Why Website Security Matters:
- Protecting Sensitive Data: Websites often collect and transmit sensitive information.This information includes login credentials, personal details, and payment data. Without adequate security measures in place, this information is vulnerable to interception by cybercriminals. This leads to identity theft, fraud, and other malicious activities.
- Building Trust and Credibility: A secure website instills trust and confidence in visitors. It demonstrates your commitment to protecting their privacy and security. In contrast, a compromised or insecure site can damage your reputation and deter potential customers from engaging with your brand.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many industries are subject to regulatory requirements regarding data security and privacy. For example, GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the United States. Implementing SSL certificates helps businesses comply with these regulations and avoid potential legal consequences.
Understanding HTTP vs. HTTPS:

HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) are protocols used for transmitting data between a web server and a browser. The key difference between the two lies in their security features:
- HTTP (Unsecured): Websites using HTTP transmit data in plain text. This makes it susceptible to interception and manipulation by cyber attackers. This lack of encryption leaves sensitive information exposed to eavesdropping and cyber theft.
- HTTPS (Secured with SSL/TLS): Websites using HTTPS encrypt data using SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security) protocols. This ensures that information exchanged between the server and the browser remains confidential and secure. HTTPS is indicated by a padlock icon in the browser’s address bar, providing users with visual assurance of a secure connection.
The Dangers of Not Securing Your Site with an SSL Certificate:
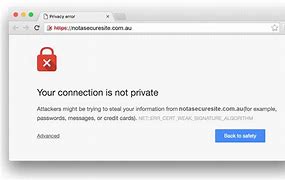
- Data Breaches: Without SSL encryption, sensitive data transmitted over insecure connections can be intercepted and stolen by cybercriminals, leading to data breaches and financial losses.
- Phishing Attacks: Cyber attackers can exploit unsecured websites to launch phishing attacks, tricking users into disclosing personal information or installing malware unknowingly.
- Loss of Trust: Insecure websites can damage your reputation and erode trust among visitors, resulting in decreased user engagement, higher bounce rates, and loss of potential customers.
- Penalisation by Search Engines: Major search engines like Google prioritise secure websites in their search rankings. Sites without SSL certificates may be penalized in search results, leading to decreased visibility and organic traffic.
Conclusively, website security is paramount in today’s digital landscape. SSL certificates play a crucial role in protecting sensitive data, building trust with visitors, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. By implementing HTTPS encryption, businesses can safeguard their websites against cyber threats and demonstrate their commitment to maintaining a secure online environment for users. Don’t wait until it’s too late! Prioritise website security today to safeguard not only your digital assets, but also reputation.

Do you need to understand more about website security, or purchase an SSL certificate, contact us. Like and share our Facebook page: https://facebook.com/onehost.digital/